These options are available in debug mode when a running program has stopped executing. While in edit mode they are greyed out and unavailable. Many options are available with keyboard shortcuts.
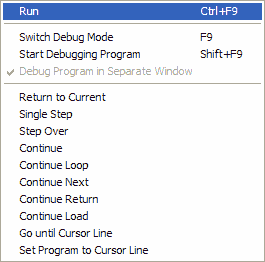
Resolves and executes the program currently in memory. Similar to the RUN immediate mode command. Also available by pressing F11 in the editor.
Switches between debug and edit mode. A switch back to debug mode can only be made if the program has not been modified. Also available by pressing F9 in the editor or debugger.
Resolves the program and positions the cursor on first line without executing it. You can then use one of the debugging commands below to step through the program. Similar to RUN STOP immediate mode command. Also available with SHIFT F9.
This is a toggle which if off by default. Normally the programs form is considered to be one of the child windows of the Workbench while the program is being debugged. This means that it will be minimized with the Workbench and you can cycle through the Workbench windows using the MDI keyboard shortcuts. However if the form contains a menu or a status bar then this may not be appropriate as an MDI application can only have one menu and thus the form may not draw properly. To correct this enable this option for such forms. The form will then be an independent window.
This will return you to the point in the program that was executing when you interrupted the program. It is useful if you have been browsing code elsewhere in the program. It can also be effected by pressing F6, possible more than once.
Steps through the program a statement at a time entering subroutines. Also available with the 'I' key.
Steps through the main body of the program a statement at a time without stepping through subroutines and skipping comments and declarations. Also available with the spacebar.
Continues program execution. Also available with the 'C' key.
Continues execution and stops it again immediately after the current WHILE ... WEND or REPEAT ... UNTIL loop is completed. Also available with the 'O' key.
Continues execution and stops it again immediately after the current FOR ... NEXT loop is completed.
Continues execution and stops it again immediately at the statement following the next subroutine call. Also available with the 'R' key.
Continues execution and stops it again immediately after the next program is loaded. Also available with the 'L' key.
Continues execution until execution reaches the current cursor line position. Also available with the 'G' key.
Moves the execution point to the current cursor line. Also available with the 'S' key.